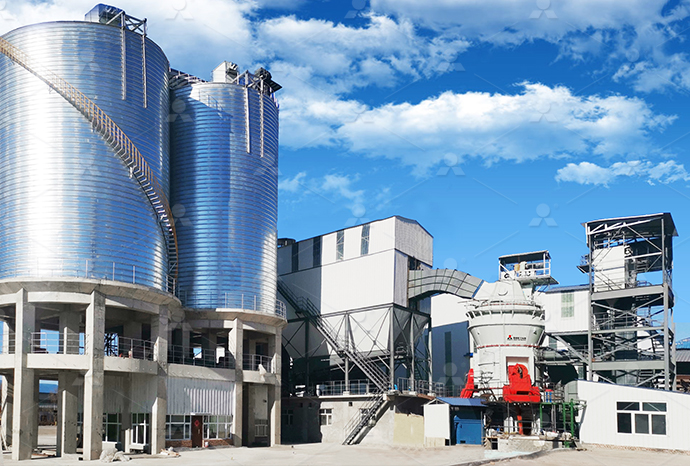
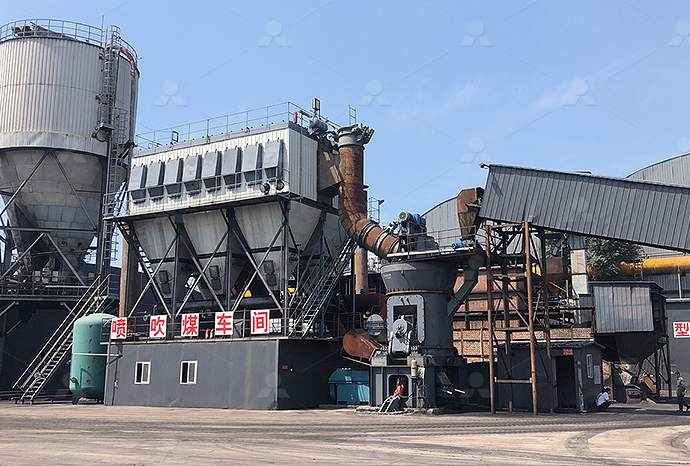
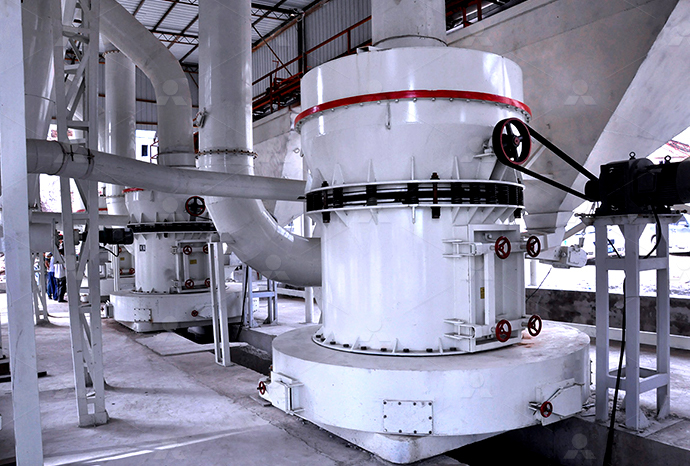
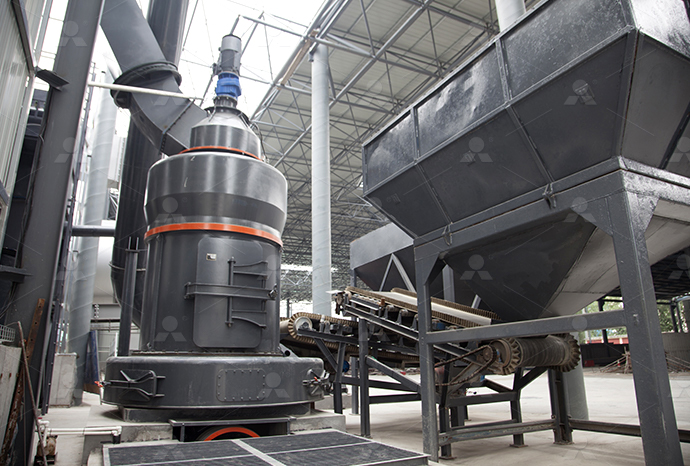
What does a coking steel plant do
.jpg)
Coking plant ArcelorMittal
In the coking plant, coal is heated to 1250c in the absence of oxygen, removing impurities and creating coke, a porous substance that is nearly all carbon Coke’s role in steelmaking is to provide the heat needed to melt the ore, whose natural state is iron oxide, the rust you see on Coking plant Coal is needed when producing liquid hot metal in the blast Coking PlantA coking plant is used to produce coke (coking coal) from metallurgical coal Coking plants consist of coke ovens (aka coking ovens, coke furnaces, coking furnaces) Coal is used to reduced Coking plant Global Energy Monitor2019年1月1日 Metallurgical coke is produced in coke ovens and is mainly used for the iron ore reduction in blast furnaces (BFs) It is also consumed in blast and electric furnaces for ferroalloy production and for the reduction of other metal Coke in the iron and steel industry ScienceDirect

How does coke and coal play into steel making?
2016年6月22日 Coke is used as a fuel and a reducing agent in melting iron ore It is produced by baking coal until it becomes carbon by burning off impurities without burning up the coal itself When coke is consumed it generates Making steel Coking plant Coke’s role in steelmaking is to provide the heat needed to melt the ore, whose natural state is iron oxide, the rust you see on iron after it has been exposed to the Coking plant ArcelorMittalCoking plant Coal is needed when producing liquid hot metal in the blast furnace However, we cannot utilise coal directly in the blast furnace as it contains a lot of harmful and unnecessary byproducts Coal is furthermore not strong enough Coking plant ArcelorMittal in BelgiumCoke is a grey, hard, and porous coalbased fuel with a high carbon content It is made by heating coal or petroleum in the absence of air Coke is an important industrial product, used mainly in iron ore smelting, but also as a fuel in stoves Coke (fuel) Wikipedia
.jpg)
Raw materials Coking plant ArcelorMittal
Coke has a dual role in the steelmaking process First, it provides the heat needed to melt the ore, and second, when it is burnt, it has the effect of ‘stealing’ the oxygen from the iron ore, leaving 2024年8月20日 Coke remains critical to the manufacturing of steel and aluminum, but it can also be used as fuel Learn more about how coal becomes coking in this guide We use essential cookies to make our site work What Is Coking? What Happens to the Coal? Cadence2013年1月28日 Coking is a refinery unit operation that upgrades material called bottoms from the atmospheric or vacuum distillation column into highervalue products and, as the name implies, produces petroleum coke—a coallike Coking is a refinery process that produces 19% of 2023年1月5日 Metallurgical coal (also called "met" coal) is an important raw material used in the steelmaking process, although very small amounts of coal (relative to the amount used for electricity) are needed The coal used to make Coal to Make Coke and Steel University of Kentucky
.jpg)
Raw materials Coking plant ArcelorMittal
To make steel in a blast furnace, coal must first be turned into coke Coke has a dual role in the steelmaking process First, it provides the heat needed to melt the ore, and second, when it is burnt, it has the effect of ‘stealing’ the oxygen from the iron ore, leaving only the pure iron behind In the coking plant, coal is heated in the absence of oxygen to 1250cA coker or coker unit is an oil refinery processing unit that converts the residual oil from the vacuum distillation column into low molecular weight hydrocarbon gases, naphtha, light and heavy gas oils, and petroleum cokeThe process thermally cracks the long chain hydrocarbon molecules in the residual oil feed into shorter chain molecules leaving behind the excess carbon in the Coker unit WikipediaSteel made in an EAF uses electricity to melt steel scrap Depending on the plant configuration and availability of steel scrap, other sources of metallic iron such as directreduced iron (DRI) or hot metal can also be used Alloying materials are used to adjust the steel to the desired chemical composition Electrical energy can be Fact sheet Energy use in the steel industryCoking, a highpolluting industry Coking process has historically been a very polluting process especially with the evolution of sulfur and nitrogen oxides from the coke ovens In Europe and the United States, only a few coking plants remain in operation and the emissions, byproducts and waste from these plants are very closely controlledCoking Industry SOLVAir®

COKEMAKING TECHNOLOGY Paul Wurth
and control systems along the entire coking process, our plants and equipment meet the highest standards in terms of coke productivity and quality, emission control, energy consumption, user friendliness and plant safety THE STATEOFTHEART OF COKEMAKING TECHNOLOGY Modern Coke Oven PlantsDemineralization of low grade coal – A review Pratima Meshram, BD Pandey, in Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2015 12 Coking and noncoking coals Coking coals are used for production of coke which is used in steel industries and noncoking coals are required for thermal power plants for steam production Coking coals are hard porous substance that Coking Coal an overview ScienceDirect TopicsIntegrated steel mill in the NetherlandsThe two large towers are blast furnaces A steel mill or steelworks is an industrial plant for the manufacture of steelIt may be an integrated steel works carrying out all steps of steelmaking from smelting iron ore to rolled product, but may also be a plant where steel semifinished casting products are made from molten pig iron or from scrapSteel mill WikipediaThe most common steel making technology is the BfBof Route Coke is used in Blast Furnace (BF) both as a reductant and as a source of thermal energy It involves reduction of ore to liquid metal in the blast furnace and and refining in convertor to form steel The various stages of the steel plant is described belowCoke OvensSinterBFBOF Route SAIL
.jpg)
Coke Plant Technologies ThyssenKrupp
Coke Plant Technologies Pioneering coke plant technologies are part of our daily business The effi ciency and environmental performance of our plants are renowned worldwide Tailor made complete coke oven plants from a single source – that’s our commitment and your advantage gained from a partnership with us 500 coking plants worldwideCoke’s role in steelmaking is to provide the heat needed to melt the ore, whose natural state is iron oxide, the rust you see on iron after it has been exposed to the atmosphere Coke also ‘steals’ the oxygen from the iron ore, so that it can become iron In the coking plant, coal is heated to 1250c in the absence of oxygen, removing impurities and creating coke, a porous Coking plant ArcelorMittalWith the new technical innovations, there was also a great hope that the coke quality can be improved significantly In particular, a higher abrasion resistance and larger quantity of particles with size above 30 mm were desirableHowever, only small improvements for the abrasion resistance and particle size could be achieved in comparison to the Lauchhammer coking plantCoking Plant an overview ScienceDirect Topics2022年1月25日 Last year was a volatile one in global commodity markets Demand for coking coal, an essential raw material in the production of steel, was extremely strong as the wider global economy recovered from its sharp contraction at the earlier height of the COVID19 pandemic—even as supply chain issues constricted availabilityHigh coking coal prices provide glimpse into steelmaking’s future

Understanding Coke Making in Byproduct Coke Oven Battery
2015年3月9日 Fig 1 Typical flow diagram of a byproduct coke oven plant Environmental issues The coke oven is a major source of fugitive air emissionsThe coking process emits particulate matter (PM), volatile organic compounds (VOCs), polynuclear aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs), methane, at approximately 100 gm/ton of coke, ammonia, carbon monoxide, hydrogen sulfide Blending of Coal: Because of limited availability of good quality coking coal, the Indian Steel plants use a optimal Blend of the 3 or more varieties of coking coal to compensate for the lack of individual coals with the necessary properties Indian Integrated Steel Plants normally use high ash coke produced inhouse, Glossary of Terms/ Definitions Commonly Used in Iron Steel %PDF16 %âãÏÓ 133 0 obj > endobj xref 133 96 00000 n 00000 n 00000 n 00000 n 00000 n 00000 n 00000 n 00000 n 00000 n 00000 n 00000 n 00000 n 00000 n 00000 n 122 Coke Production US Environmental Protection Agency2012年4月2日 Coke Oven Emissions FF Farris, in Encyclopedia of Toxicology (Third Edition), 2014 Abstract Coke oven emissions are the volatile products that are released from bituminous coal during its conversion to coke in high temperature ovens in the absence of air These emissions arise from the noncarbonaceous materials present in the coal prior to processing Coke Oven an overview ScienceDirect Topics

Coking 101 An Introduction to Delayed Coking
Coking 101 An Introduction to Delayed Coking Prepared By: : info@ProcessEngr ProcessEngr Adams Project Managers, Inc fuel in power plants Adams Project Managers, Inc VI Coke Drum Deheading 12 The modern Coker has automatic deheading valves on the top and bottom cokeCoke Coking coal is converted to coke by driving off impurities to leave almost pure carbon The coking coal is crushed and washed It is then ‘purified or ‘carbonised in a series of coke ovens, known as batteries, where the coking coal is heated to 10001100ºC in the absence of oxygen for 1236 hoursCoal steel FutureCoalSteel is primarily produced using one of two methods: Blast Furnace or Electric Arc Furnace The blast furnace is the first step in producing steel from iron oxides The first blast furnaces appeared in the 14th century and produced one ton Steel Production American Iron and Steel InstituteCoking plant Coal is needed when producing liquid hot metal in the blast furnace However, we cannot utilise coal directly in the blast furnace as it contains a lot of harmful and unnecessary byproducts Coal is furthermore not strong enough Coking plant ArcelorMittal in Belgium
.jpg)
Chemistry and geology of coal: nature, composition, coking
does not exist by itself (with the exception of some adsorbed methane), but denotes the volatile compounds that are formed and expelled when the coal is heated For economic reasons, it is important to know the moisture and ash content of coal as they do not contribute to 2024年3月17日 Steel making is a sophisticated process that turns iron ore into steel, Its quality and purity influence the efficiency of the reduction process and the overall quality of the steel produced Coal: Specifically the coking variety, Advancements such as closedloop water systems in plants aim to minimize water usage and pollutionA Visual Guide: Steel Making Process Chart Cabaro Group2023年1月23日 CMM adds 27% to steel’s global warming impact Mines producing coking coal emitted nearly 12 million tonnes of methane in 2021, according to the IEA This is equivalent to nearly 990 million tonnes of CO2 using the IPCC’s 825 multiplier for methane’s 20year climate impact versus carbon dioxideWhy the steel industry needs to tackle coal mine methaneA delayed coker is a type of coker whose process consists of heating the residual oil feed to its thermal cracking temperature in a multi parallel pass furnace This cracks the long chain heavy carbon and hydrogen molecules of the residual oil into coker gas oil and pet coke Cracking begins in the furnace, continues in the transfer line, and finishes in the coke drum (wikipedia Coking » Delayed Coker Unit (DCU)
.jpg)
Coke plant technologies thyssenkrupp Uhde
Jinhui Coal Coking Co Ltd Xiaoyi, PR China (Completion 2021) Capacity: 2,100,000 t/year, 140 ovens, JFE Steel Corporation Kurashiki, Japan (Completion 20102015) Capacity: and commissioning of a pushing emissions control system including optimised sequence planning to avoid lengthy plant stoppage times JFE Steel Corp2019年1月1日 The BF ironmaking including sintering and coking plants is the most energy consuming process at an integrated steel plant It consumes about 65%–75% of the entire energy in integrated steelworks (Babich et al, 2016) The main part of the required energy is covered by metallurgical cokeCoke in the iron and steel industry ScienceDirect22 Conventional coking plant – byproduct plant Byproduct coking plants are comprised of single oven chambers, being 12 to 20 m long, 3 to 8 m tall, and 04 to 06 m wide, in which the input coal is heated up indirectly Several chambers are grouped to form one battery (multichambersystem; Fig 4) A single batteryEnvironmental Control and Emission Reduction for Coking Plants 2024年9月12日 Second furnace closed, Vizag Steel Plant on the verge of total shutdown The available coking coal stock in its yard, to run the last of its three furnaces, is expected to barely last for fivesix Second furnace closed, Vizag Steel Plant on the verge
.jpg)
Why Europe doesn’t need Cumbria’s coking coal Inside track
2016年8月26日 Most of today’s coking coal consumers are looking for alternatives and the European steel sector is becoming more circular It is a myth that steel production requires coking coal A third of global steel today is made without coking coal, either through scrap recycling or gasbased steel production; and countingRashtriya Ispat Nigam Ltd (abbreviated as RINL), also known as Vizag Steel, is a central public sector undertaking under the ownership of Ministry of Steel, Government of India based in Visakhapatnam, IndiaRashtriya Ispat Nigam Rashtriya Ispat Nigam WikipediaA 4drum delayed coking unit in a petroleum refinery A delayed coker is a type of coker whose process consists of heating a residual oil feed to its thermal cracking temperature in a furnace with multiple parallel passes This cracks the heavy, long chain hydrocarbon molecules of the residual oil into coker gas oil and petroleum coke [1] [2] [3] Delayed coker WikipediaProduction normally takes place in a coke battery located near an integrated steel mill In the battery, coke ovens are stacked in rows Coal is loaded into the ovens and then heated in the absence of oxygen up to temperatures around 1,100 degrees Celsius (2,000 degrees Fahrenheit) Without oxygen, the coal does not burn; it begins to meltCorsa Coal Corp Coal in Steelmaking
.jpg)
Coke Oven Gas Generation and Usage IspatGuru
Coke oven gas forms a major component in the energy balance of the steel plant It is normally used in coke oven battery heating, heating in other furnaces of the steel plant, and for power generation Coke oven gas can be used as such or can be mixed with the blast furnace gas before being used as fuel in a furnace2022年8月5日 Currently, conventional oil is used as the main source for the petrochemical industry However, conventional oil’s capacity is declining, and that source will probably be exhausted in the near future Heavy oil and petroleum residues have become a suitable alternative source to meet global energy demand However, heavy oil and oil residues require Coking IntechOpenLearn about Tata Steel UK's sustainability performance at Port TalbotPort Talbot Tata Steel UK2023年4月7日 The UK steel industry is at a turning point a way of life is already lost for many former workers But if it can be resurrected as a powerful motor of a green economy, it's a tantalising prospectWhy the British steel industry is on the brink of extinction or a

Coal facts Canada
2024年5月21日 Coal is an organically derived material formed from the remains of decayed plant material that were compacted into a solid form through Higher carbon and lower moisture coal is often used to make steel Coal used for steelmaking is commonly referred to as metallurgical or coking coal Key facts Coal is used mostly for