Peat soil production process
.jpg)
Peat formation International Peatland Society
Peat formation is the result of incomplete decomposition of the remains of plants growing in waterlogged conditions This may happen in standing water (lakes or margins of slow flowing rivers) or under consistently high rainfall (upland or 2018年9月19日 Peat soil or commonly referred to as organic soil is a soil formed from decomposed plant parts accumulated over thousands of years in waterlogged soil conditions [1](PDF) Introductory Chapter: Introduction to Peat ResearchGate2023年6月15日 Four classes of processbased (or equivalently physically based) models can be identified that simulate peatland dynamics: (i) climate models; (ii) Land Surface Models Peatland dynamics: A review of processbased models and The process of peat formation as a result of waterlogged conditions is called paludification The major factors playing a role in this process are discussed below According to Moore and 3 FORMATION OF PEATS Food and Agriculture Organization
.jpg)
Peat and organic soil The Biology of Peatlands Oxford Academic
2006年6月8日 Peats are organicrich materials that have accumulated on wet, oxygenpoor substrates by sedentary processes Organic matter content, the inverse of which is ash Peat is used in horticulture, as a soil improver and ingredient of growing media The volume used annually is about half that of fuel peat Germany and Canada account for over half of Peat International Peatland SocietyIt first considers the process of peat formation by organic matter through sedentation and sedimentation before comparing the organic versus mineral matter content of peat It then Peat and organic soil The Biology of Peatlands Oxford Academic2022年9月28日 This review identifies key research gaps, including underrepresented geographic areas and peat properties and highlights the need for standardised methodologies for Differences in Tropical Peat Soil Physical and Chemical Properties
.jpg)
Structure of peat soils and implications for water storage, flow
2016年7月1日 Dualporosity concept of peat soil including a “mobile region” with advective flow and an “immobile region” that exchanges solutes with the mobile region via of CH 4 and DIC from methanic microniches into the active porosity may therefore represent a key ratecontrolling process for the production of methane in peatlandsThe peat deposits are found to be distributed in many countries all over the world, occupying nearly 5%–8% of land surface of the Earth (Mesri and Ajlouni, 2007)A recent study on peatland mapping has reported that the total area of the peatland is 423 million km 2 (Xu et al, 2018), and the major distributions are summarized in Table 41A high distribution of peatlands can Peat Soil an overview ScienceDirect Topics2018年5月4日 According to Holman , there are four types of peat soil: (i) deep peat – peat soils thicker than 100 cm from surface, (ii) thin peat – peat soils thinner than 100 cm from surface, (iii) peat at depth –peat layers of more than 30 cm thickness embedded within the soil horizons of generally alluvial mineral material, and (iv) remnant peat –peat soils that have been left after Peat Soils SpringerLink2024年2月15日 Benefits of Coco Peat Sustainable Alternative: Coco peat is an ecofriendly alternative to traditional soilbased growing mediums By utilizing coconut husks, which would otherwise be discarded, coco peat production helps reduce waste and promotes sustainable practices Excellent Water Retention:Crafting Coco Peat: Unveiling the Coconut Transformation Process
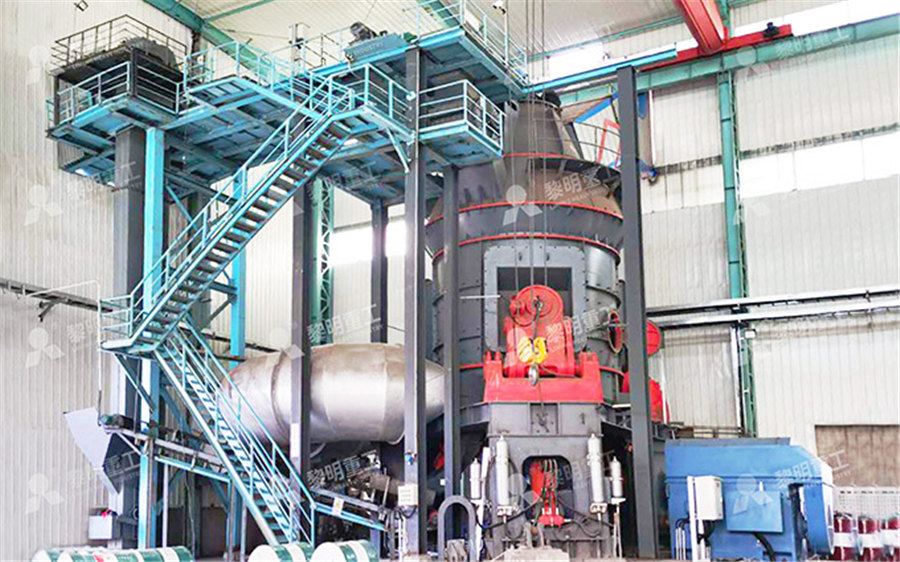

What are peatlands? International Peatland Society
Peatland is a terrestrial wetland ecosystem in which the production of organic matter exceeds its decomposition and a net accumulation of peat results Peatlands occur in every climatic zone and continent The total area globally is around 4 million km2 making them 70% of natural freshwater wetland or 3% of the Earth’s land surface Peatlands include landscapes that are still actively 2023年8月17日 Peat moss is a natural resource formed over thousands of years through the decomposition of organic material in peatlands Understanding the production process of peat moss is essential for appreciating its value and the impact of its commercial use on the environment Peat moss is harvested from peatlands, which are wetlands that accumulate How is Peat Moss Made? Discover the Natural Formation ProcessPeat is used in horticulture, as a soil improver and ingredient of growing media The volume used annually is about half that of fuel peat Germany and Canada account for over half of horticultural peat extraction Other important peat production countries are the Baltic states, Finland, Ireland and Sweden but also Chile and ArgentinaPeat International Peatland Society2019年10月3日 Peat is intermediate between soil formation (soil) and brown coal From the first it differs by the presence of organic compounds – more than 50% of dry substance, and from second to high moisture content and poorly decomposed organic residues of plants, and the presence of cellulose , carbohydratesPeat, formation, properties, types, production and application

BG Effects of sterilization techniques on chemodenitrification and
2019年12月5日 Abstract Chemodenitrification – the nonenzymatic process of nitrite reduction – may be an important sink for fixed nitrogen in tropical peatlands Rates and products of chemodenitrification are dependent on O2, pH, Fe2+ concentration, and organic matter composition, which are variable across peat soils Assessing abiotic reaction pathways is Soil health and management In Lockhart and Wiseman' s Crop Husbandry Including Grassland, 2023 346 Peat and peaty soils These soils are dominated by high quantities of organic matter that produce key characteristics Peaty soils (peaty loam and peaty sand) contain about 20%–35% of organic matter, whereas there is 35%–50% in loamy peat and sandy peat and Peat Soil an overview ScienceDirect Topics2024年5月8日 Background and Aims Peatlands occupy only 3% of Earth’s terrestrial lands but store about onethird of global soil carbon However, these large carbon stocks are currently under threat due to peatland degradation, where altered hydrological balance could enhance peat oxidation; thus releasing large amounts of CO2 into the atmosphere We investigated the Organic matter decomposition in mountain peatlands: effects of COCO PEAT VIETNAM; COCO PEAT FACTORY – COCO HITECH VIETNAM COCO HITECH is proud to be top coco peat block, coco peat brick, coco peat open top bag coco coir, coco peat slab, coco peat bag in Vietnam If you COCO PEAT PRODUCTION PROCESS

BIOCHAR REPLACES PEAT IN HORTICULTURE: ResearchGate
replacement for peat in soilfree substrates at high rates (70% total substrate volume) for marigold production Since thermal technologies are still scaling up, commercialFrom husk to horticulture: The production process of coco coir Coco coir, also known as coco peat or simply coir, is a growing medium that is made from the fibrous husks of coconutsThese husks are the outer layer of the coconut By processing these husks into a fibrous, soillike material, they can be transformed into a highly effective growing medium that is perfect for a From husk to horticulture The production process of coco coir2020年1月1日 It is a viable ecologically friendly peat soil substitute for containerized crop production The multipurpose growing media had received much interest particularly in commercial applicationsLocally Produced Cocopeat Growing Media for Container Plant Production2024年9月2日 1:1 – This is the most common ratio for general use It is a good balance of Coco Peat and soil that can be used for most plants 2:1 – This ratio is often used for plants that require more drainage, such as succulents The higher Coco Peat content helps to keep the soil loose and drains excess water more effectivelyHow to Make Coco Peat at Home: Process, Steps, and Guide
.jpg)
Introductory Chapter: Introduction to Peat IntechOpen
2018年9月19日 1 Peat formation and characteristics The word known peat is growth on organic systems where the plant growth is fast, but soils are defined as a partially decomposed organic matter deposit due to poor aeration and low temperature grades []Peat is also named as turf and turba in different literatures owing to its unique property to natural areas called peatlands, 2022年9月13日 Peat structure The process of peat formation is the result of longterm accumulation of organicrich, partly decomposed plant material forming a soil matrix that slows down water movement across Ecological resilience of restored peatlands to climate changeThere are many ways to make coco peat, but the production process generally begins by collecting coconut coir, which is the fiber on the coconut husk Most manufacturers collect coco peat through a process that looks like this: Collect coconuts from the trees and store for a sixweek curing process Peel the outer layer of the husk from the How is Coco Peat Made? Coir2019年8月2日 Effects of sterilization techniques on chemodenitrification and N2O production in tropical peat soil microcosms August 2019 Biogeosciences Discussions(PDF) Effects of sterilization techniques on ResearchGate
.jpg)
Effects of sterilization techniques on chemodenitrification and N 2
Chemodenitrificationthe nonenzymatic process of nitrite reductionmay be an important sink for fixed nitrogen in tropical peatlands Rates and products of chemodenitrification are dependent on O 2, pH, Fe 2+ concentration, and organic matter composition, which are variable across peat soils Assessing abiotic reaction pathways is difficult because sterilization and inhibition agents 2023年10月23日 Coco peat, a versatile and ecofriendly growing medium, begins its journey from humble coconut husks Understanding the manufacturing process of coco peat sheds light on its sustainable and beneficial qualities In From Coconut to Coco Peat: The Manufacturing 2021年4月14日 The peat degradation continues as long as low water tables are maintained and a once pristine peat with almost 100% organic matter turns into a mineral soil with less than 30% organic matter There is much more to peat Peat soils: Climate killer or climate saver? Open 2018年10月1日 Peat erosion is a natural process driven primarily by actions of water and wind, but slight changes in conditions driven by human action can lead to accelerated erosion and degradation (Parry et al, 2014)Wind erosion can occur where the peat surface is largely bare and is common in windy uplands and peat mining areas (Foulds and Warburton, 2007a; Erosion in peatlands: Recent research progress and future directions
.jpg)
German company seeks production partner to produce a sustainable peat
2024年10月30日 German company seeks production partner to produce a sustainable peat alternative using a new process Summary Profile Type Technology offer; POD Reference TODE Term of Validity A German company developed an innovative and sustainable method for soil and substrate production, along with its special humus product2021年1月29日 Peatlands are significant carbon (C) stores, playing a key role in naturebased climate change mitigation While the effectiveness of nonforested peatlands as C reservoirs is increasingly Peat deposits store more carbon than trees in forested Nature2024年2月9日 Peat soil is formed through a complex and gradual process that takes place in wetland areas with high water content and low oxygen levels The formation of peat soil begins with the growth and death of various types of plant What Is Peat Soil Chicago Land Gardening2024年1月23日 Sazawa, K et al Impact of peat fire on the soil and export of dissolved organic carbon in tropical peat soil, Central Kalimantan, Indonesia ACS Earth Space Chem 2 , 692–701 (2018)Elevated methane flux in a tropical peatland postfire is linked to

Coco Peat Manufacturing Grow By Coco
2015年8月2日 Once the moisture of coco peat become below 18%, the coco pith is sent for final screening Coco Peat Final Screening In the final screening / sieving process, the sand is removed by using our screeners Since it’s the final screening process, the coco peat is thoroughly tested for any impurities or bigger coco husks Coco Peat Compressionon a drymass basis (Paavilainen and Paivanen, 1995) Peat soil is composed of partly decomposed biomass and found in depressions when the rate of biomass production from adapted vegetation is Management and conservation of organic peat soils for Step 1: Coconut Husk Processing Coconut husks are processed at our Coconut Fibre Mills to extract coir fibre, leaving behind the byproduct – a spongy material that binds the coconut fibre in the husk – the coco coir or the coco peat, the main raw material for Coco Peat Manufacturing Fibre Family2024年9月30日 The peat soil samples taken from this depth represented the soil above the water table level in an oil palm plantation, which was generally controlled between 50 and 70 cm depth At the forest site, samples were Tropical peat soil changes across successive oil palm
.jpg)
What is Coco Peat Soil? Benefits, Uses And How to
2023年7月31日 3 Reduced Soil Degradation: Traditional peat extraction disrupts natural peat bogs, leading to soil degradation and loss of important ecological functions On the other hand, coco peat production repurposes 2024年3月15日 Peatlands, on the other hand, have the unique ability to sequester carbon, acting as natural carbon sinks Their waterlogged conditions slow down the decomposition of plants, allowing for the accumulation of dead plant material as peat soilThis process effectively removes carbon from the atmosphere and stores it within the peatlandsPeat Energy Production Its Climate Impact2023年10月17日 Know the Process of Making Coco Peat at Home: StepbyStep Guide, Sourcing Raw Materials for Coco Peat Production and more Know the Process of Making Coco Peat at Home: StepbyStep essential nutrients, while perlite or vermiculite improves aeration and drainage Another option is to mix coco peat with garden soil in a 1:1 ratioKnow the Process of Making Coco Peat at Home: StepbyStep 2022年11月12日 To retain moisture, add coco peat to potting mix or soil To make seed starting mix, combine coco peat with perlite or vermiculite As an alternative to sphagnum moss, use coco peat to line wire baskets for hanging plants Coco peat can also be used as a mulch around plants This helps to keep the soil moist and smothers any weeds that have What is Coco Peat? How to Use Coco Coir Soil for Planting

Climate warming and elevated CO2 alter peatland soil carbon
2023年11月20日 No inherently stable peat soil carbon or due to changes in plant production and thus litter inputs to SOC 11,16,17 Soil warming, occurring more rapidly at high compared to low latitudes 2019年3月8日 Methane is a major product of the anaerobic degradation of organic matter in peatlands and produced by methanogenic archaea The activity of methanogens in peatlands can easily be detected, because methanogenic metabolic activity is directly related to the amount of CH 4 produced in peat Measurements of potential methane production show that Methanogenesis in Soils, Wetlands, and Peat SpringerLinkNitrous oxide (N2O) in soils is produced through nitrification and denitrification The N2O produced is considered as a nitrogen (N) loss because it will most likely escape from the soil to the atmosphere as N2O or N2 Aim of the study was to quantify N2O production in grassland on peat soils in relation to N input and to determine the relative contribution of nitrification and Nitrogen loss from grassland on peat soils through nitrous oxide productionPeat is typically used as both fuel and as a soil enricher Why is peat used to make whisky? says little about how many phenols and thus peat aromas are in the final whisky and how smoky it actually is as the production process and variation within can significantly reduce the final PPMPeat whisky Whiskipedia